How to Choose Best Home Router
How to Choose Best Home Router
Blog Article
These days, every home must have a reliable high-performing Wi-Fi router. By connecting all of your devices and controlling your online activity, your router works as a gateway to the Internet. Regretfully, there are a lot of choices available to you, which has made it more challenging to find a router that meets your needs. I tried to provide as much information as I could on the features and capabilities of home routers in this post so that you could review the specs of the many routers on the market, compare them, and choose the best one.
This tutorial in wifiadviser.com will clarify for you which router is required for basic web browsing and which is required for streaming large videos and playing online games. In addition to this, we discuss each router’s coverage level and the maximum number of users it can accommodate. Come along with us to become an expert in router selection.
1. Assessing Your Home’s Size
We’ll start by discussing a router’s coverage level, which is its most crucial feature. Depending on its cost, technology, and antenna count, each router has a specific and restricted coverage capacity. As a result, you should base your router selection on the size of your house. The following describes how different house sizes will impact your router selection:
Small Homes (Apartments/Condos)
You can utilize a conventional router with limited coverage in small homes like apartments or condos, which have few walls and obstructions.
- Recommended Routers: Entry-level ones with minimal coverage and range.
- Features to Look For: Reliable performance, small size, and ease of setup.
- Coverage Needs: Approximately 1,000-1,500 square feet.
Medium Homes (Single-Story Houses)
Routers with higher output power are required for medium-sized homes, which typically have a single floor. These homes typically have a modest terrace, a yard, and several walls.
- Recommended Routers: Mid-range models with stronger output power.
- Features to Look For: Good obstacle penetration, multiple antennas, and increased range.
- Coverage Needs: Approximately 1,500-3,000 square feet.
Large Homes (Multi-Story Houses)
Large homes may have multiple floors, which makes it difficult to have enough Wi-Fi coverage. There are undoubtedly a large number of users who may be in different parts of the house or moving between floors and rooms.
- Recommended Routers: High-end models or mesh WiFi systems.
- Features to Look For: Extended range, additional nodes or satellites, and seamless connectivity across floors.
- Coverage Needs: Over 3,000 square feet.
Summary Table
| Home Size | Recommended Router Type | Key Features | Coverage Area |
| Small Homes | Basic Router | Compact, easy setup, reliable performance | 1,000-1,500 square feet |
| Medium Homes | Mid-Range Router | Enhanced range, multiple antennas, good obstacle penetration | 1,500-3,000 square feet |
| Large Homes | High-End Router or Mesh System | Extended range, additional nodes, seamless multi-floor coverage | Over 3,000 square feet |
You may select the ideal router to guarantee powerful, dependable WiFi throughout your whole living area by taking into account the size of your house and being familiar of the coverage needs. No matter where you are in your house, this guarantees a flawless online experience for all of your activities.
2. Simultaneous Users and Devices
The most crucial consideration when selecting a router type is the quantity of individuals and devices connected simultaneously. Smartphones, tablets, laptops, smart TVs, and other smart home appliances are among the many gadgets that are frequently linked to the Internet simultaneously in modern households. The number of concurrent users and devices connected to your network is a crucial factor to take into account when selecting the finest home router.
Small Households (1-5 Devices)
A typical router with a moderate amount of processing power is adequate to service small houses with few devices. Basic tasks like social networking, video streaming, and web browsing are simply managed by these routers.
- Recommended Routers: Basic to mid-range models.
- Key Features: Dual-core processor, 1 GHz, 128-256 MB RAM.
- Speed Recommendation: Overall speed around 3000 Mbps.
Medium Households (5-15 Devices)
Generally speaking, medium-sized households have more devices connected at once and may be capable of more demanding tasks concurrently. Smart home gadgets may be in use at home, and many users may watch high-quality videos and play online games. To guarantee lag-free functioning in this scenario, a stronger router with greater processing and memory is needed.
- Recommended Routers: Mid-range models with higher capacity.
- Key Features: Dual-core processor, 1.5 GHz, 256-512 MB RAM.
- Speed Recommendation: Overall speed around 5000 Mbps.
Large Households (15-25 Devices)
Computers, game consoles, smart TVs, and other smart home appliances are also common in large homes. They want a high-performance router in this scenario that can handle several high-bandwidth operations concurrently and offer seamless service to every user.
- Recommended Routers: High-end models or mesh systems.
- Key Features: Quad-core processor, 1.8 GHz or higher, 512 MB RAM or more.
- Speed Recommendation: Overall speed around 8000 Mbps.
Crowded Homes (25+ Devices)
A high-performance router is essential for a busy household with over 25 devices connected to the internet. To manage significant network traffic, this device should offer the fastest speeds and the greatest performance.
- Recommended Routers: Premium models or advanced mesh systems.
- Key Features: Quad-core processor, 2 GHz or higher, 1 GB RAM or more.
- Speed Recommendation: Overall speed around 10000 Mbps.
Summary Table
| Household Size | Recommended Router Type | Key Features | Speed Recommendation |
| Small Households | Basic to Mid-Range Router | Dual-core processor, 1 GHz, 128-256 MB RAM | Overall speed around 3000 Mbps |
| Medium Households | Mid-Range Router | Dual-core processor, 1.5 GHz, 256-512 MB RAM | Overall speed around 5000 Mbps |
| Large Households | High-End Router or Mesh System | Quad-core processor, 1.8 GHz or higher, 512 MB RAM or more | Overall speed around 8000 Mbps |
| Crowded Homes | Premium Router or Advanced Mesh System | Quad-core processor, 2 GHz or higher, 1 GB RAM or more | Overall speed around 10000 Mbps |
Considerations for Choosing the Right Router
- Processing Power: A router with more processing power can manage more devices without experiencing any lag.
- RAM: More RAM makes it easier to handle several connections and high-bandwidth tasks at once.
3. Understanding Radio Bands
Three radio bands are available on modern routers; each band has unique benefits and drawbacks that should be taken into account when making a decision. 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and the more recent 6 GHz spectrum are these bands.
2.4 GHz Band
The oldest and most used frequency range for WiFi networks is 2.4 GHz. Larger homes and places with a lot of obstructions are better suited for this band because it has the most penetration and range( Lower frequencies are stronger). Keep in mind that the Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, and microwaves use this frequency; Consider in mind that this band has the most frequency congestion.
- Advantages:
- Improved penetration and coverage via walls and barriers .
- Compatible with the majority of WiFi devices.
- Disadvantages:
- More vulnerable to interference than other frequencies.
- More limited than other frequency bands.
5 GHz Band
Compared to the traditional 2.4 GHz band, the 5 GHz offers more speed and bandwidth, because of higher frequency. High-bandwidth activities like streaming HD videos and playing online games are appropriate for this frequency range. At the other hand, it has less penetration and a shorter range.
Advantages:
- More bandwidth and faster speeds for demanding applications.
- Reduced interference from other electronic devices in the home.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited range and reduced penetration ability.
- The 5 GHz spectrum is not supported by older devices.
6 GHz Band
WiFi 6E ( Introduced with WiFi 6 Standard) supports 6 GHz frequency band, which is less congested and offers higher speeds. Applications like virtual reality, 8K streaming, and massive file transfers are better suited for this band’s faster speeds. Because the 6 GHz spectrum is less busy, there can be less interference.
- Advantages:
- Fastest speeds and minimal latency.
- Reduced interference and congestion.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited range and low wall penetration capability.
- Limited compatibility because this band is only supported by more recent devices.
Choosing the Right Band
Your particular demands will determine which radio bands are best for you, but if you have a 3-band router, it is preferable to connect to the 2.4 GHz band for basic tasks like email and online browsing. To work with high-quality contents and online games, connect to the 5 GHz band. For tasks like watching Ultra-Quality 8K videos and using virtual reality, connect to the 6 GHz band.
- Single-Band Routers: Only works on 2.4 GHz frequency band.
- Dual-Band Routers: Equipped with 2 bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands are available simultaneously.
- Tri-Band Routers: 4 GHz, 5 GHz, and an extra 5 GHz band, or 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands, are available.
Tri-Band Routers Explained
These routers have 3 different bands, One 2.4 , one 5 GHz and for particular purposes, an additional frequency band on 5 GHz or 6 GHz.
- 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 5 GHz Configuration:
Example Use:
- Band 1 (2.4 GHz): General web browsing, social media, and email.
- Band 2 (5 GHz): Streaming HD/4K videos, online gaming.
- Band 3 (5 GHz): Additional high-bandwidth activities, ensuring no single band is overloaded.
- 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, 6 GHz Configuration:
Example Use:
- Band 1 (2.4 GHz): General web browsing, social media, and email.
- Band 2 (5 GHz): Streaming HD/4K videos, online gaming.
- Band 3 (6 GHz): High-bandwidth applications like VR, 8K streaming, and large file transfers.
Summary Table
| Band | Advantages | Disadvantages | Ideal For |
| 2.4 GHz | Better coverage and penetration, wide compatibility | More interference, limited bandwidth | Larger homes, basic internet usage, older devices |
| 5 GHz | Higher speeds, less interference | Shorter range, less effective at penetrating walls | Streaming HD videos, online gaming, newer devices |
| 6 GHz | Highest speeds, lowest latency, less congestion | Shortest range, limited compatibility | VR, 8K streaming, large file transfers, latest devices |
| 5 GHz (Extra) | Additional bandwidth, reduced congestion, load balancing | Shorter range, less effective at penetrating walls | Additional high-bandwidth activities, multiple devices |
4. Speed (Wireless Protocols)
The speed at which data can travel between devices and the Internet depends on your router’s speed, and wireless protocols specify the standards and technologies that are employed to reach these speeds. The seven standards that the Wifi Alliance has so far developed have changed dramatically over time, with each new generation bringing faster, more capable, and more efficient rates. An outline of the most widely used wireless protocols is provided below:
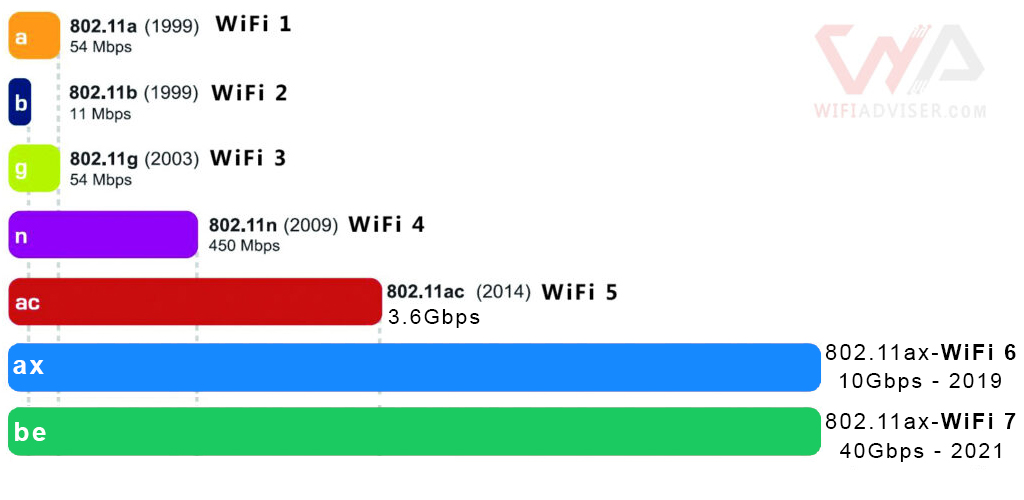
Wireless Protocols Overview Table
| Wireless Protocol | Maximum Speed | Frequency Bands | Key Features | Ideal For |
| Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n) | Up to 600 Mbps | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz | MIMO | Basic internet usage, SD streaming, light gaming |
| Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) | Up to 3.5 Gbps | 5 GHz | Beamforming, MU-MIMO | HD streaming, online gaming, smart home devices |
| Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) | Up to 9.6 Gbps | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz | OFDMA, improved MU-MIMO | 4K/8K streaming, VR/AR, dense device environments |
| Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax) | Up to 9.6 Gbps | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz | Additional 6 GHz band, reduced congestion, lower latency | Future-proofing, high-bandwidth applications, smart home integration |
| Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) | Up to 40 Gbps | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz | Enhanced OFDMA, multi-link operation, higher capacity | Ultra-high definition streaming, extensive smart home setups, industrial applications |
Factors Affecting Router Speed
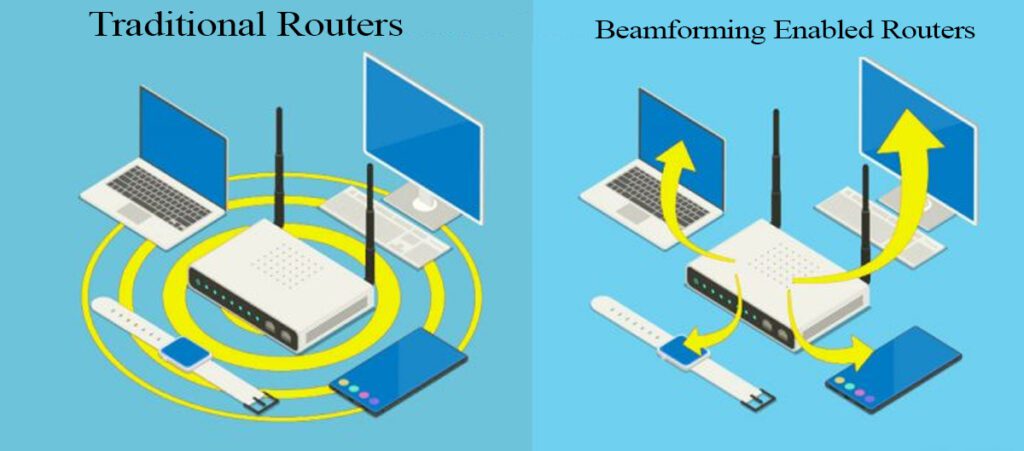
- Beamforming:
- Instead of broadcasting the WiFi signal in all directions, beamforming directs the signal to the devices that are connected. This focused strategy increases signal strength, which leads to better performance and higher speeds, particularly over longer distances.Read More : What is Beamforming?
- MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output):
- Instead of serving the connected devices one at a time, MU-MIMO technology enables the router to communicate with and service several devices concurrently. Users’ bandwidth is greatly increased by this.

- OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access):
is a feature of Wi-Fi 6 that enables data to be sent to several devices at once by splitting a WiFi channel into smaller subchannels. By making effective use of the available bandwidth, latency is decreased and network speed and capacity are increased overall.
Understanding Router Speeds
The router’s speed is expressed as a sum of its theoretical and cumulative speeds. Stated differently, what is the total bandwidth of all router bands under optimal circumstances? For instance, if a Dual-Band router has a speed label that reads 3000 Mbps, it indicates that the combined communication speed of its two bands is 3000 Mbps (about 600 Mbps in the 2.4 GHz band and 2400 Mbps in the 5 GHz band).
5. Exploring Mesh Technology
A revolutionary development in WiFi networks is mesh technology. It provides a practical way to maximize and extend WiFi coverage in big or multi-story buildings. Several routers work together to generate an impressive Wi-Fi network, making it invisible to the users the number of probable routers and just see one unified wifi network.
The network is designed to ensure that consumers will not experience any disruptions while switching between routers and that their service quality will not become weaker. Second, users in such a network are immediately linked to the closest router and always get the greatest signal; third, adding a router can increase the network’s accessibility.
Mesh Technology Overview: This diagram shows how a mesh WiFi network uses a main router and satellite nodes to deliver consistent and reliable WiFi coverage across the entire home.
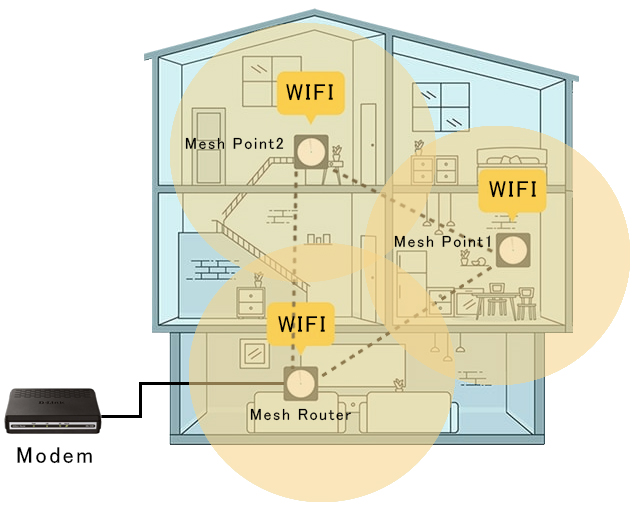
| Component | Placement | Function |
| Main Router (Mesh Router) | Centrally in the home | Connects to modem, distributes internet to satellite nodes |
| Satellite Nodes (Mesh Point) | Throughout the home (e.g., upstairs, basement) | Extend WiFi signal, eliminate dead spots |
6. Checking Ports and Connectivity Options
The quantity and kind of ports as well as the available connectivity alternatives should be taken into account when selecting the most suitable home router. The performance and value of your router can be greatly impacted by these characteristics, which also dictate how you can connect various devices to your network.
Types of Ports
| Port | Function | Consideration |
| LAN Ports | Allow you to connect wired devices directly to your router (e.g., gaming consoles, desktop computers, smart TVs). | Make sure the router has enough LAN ports for all your wired devices; Consider multi-gigabit ports for faster connections |
| WAN Port | Connects your router to the modem, providing internet access to all connected devices. | Look for routers with gigabit WAN ports to take full advantage of high-speed internet plans. |
| USB Ports | Used for connecting external storage devices, printers, or creating a media server. | Check if the router supports USB 3.0 for faster data transfer speeds compared to USB 2.0. |
| SFP Ports | Connect to fiber optic networks, offering higher speeds and more reliable connections. | Typically found in premium routers; beneficial if you have access to fiber optic internet. |
Router Port Types: This diagram shows different port types found on a router
Wireless Connectivity Options
| Connectivity Option | Function | Consideration |
| Backhaul | Allows you to connect multiple mesh nodes or routers using an independent frequency band. | Particularly useful in large homes where cabling is not possible. |
| Bluetooth and Zigbee Integration | Acts as a smart home hub for connecting and controlling various smart home devices directly through the router. | Simplifies smart home setup by reducing the need for multiple hubs and devices. |
7. Parental Controls
For many families, parental controls are a fundamental and significant feature that allows us to keep an eye on how family members—especially kids—use the Internet. With the help of this function, you can manage user behavior on the Internet, restrict access to particular websites, determine when users are permitted to use the Internet, and restrict a range of applications or particular types of information.
Parental Control Features
| Feature | Function | Consideration |
| Website Filtering | Blocks access to inappropriate or harmful websites based on categories or specific URLs | Customizable filters tailored to your family’s needs |
| Content Filtering | Filters out specific types of content (e.g., adult content, violence, gambling) | Easy updates to filtering lists to keep up with new websites and content types |
| Time Scheduling | Sets time limits for internet usage, controlling when specific devices can access the internet | Flexible scheduling options, such as daily or weekly limits |
| Device-Specific Controls | Applies different restrictions and settings to individual devices | Tailoring controls to the age and needs of each family member |
| Usage Monitoring and Reports | Monitors internet usage and provides reports on websites visited and time spent online | Detailed and easy-to-read reports to stay informed about online activities |
8. QOS / Traffic Shaping
Traffic prioritization and quality of service (QoS) are crucial and useful features to maximize home network performance. For instance, online gaming services are always assured of the bandwidth they require
QoS and Traffic Shaping Features
| Feature | Function | Consideration |
| Traffic Prioritization | Assigns higher priority to essential applications and devices | Customizable and user-friendly interface |
| Application-Based QoS | Automatically prioritizes traffic for specific applications | Built-in profiles for common applications |
| Device-Based QoS | Prioritizes traffic based on the device | Assign priority levels to different devices |
9. Prioritizing Ease of Use and Setup
Since not every user is a professional who can solve complicated installation issues, ease of use and simplicity are two of the most crucial considerations when selecting a good home router. Generally speaking, routers with easy-to-use control consoles are more popular; routers with complex management consoles are not suitable for all users.
Ease of Use and Setup Features
| Feature | Function |
| Simple Installation Process | Guides you through the installation process with step-by-step instructions |
| User-Friendly Interface | Provides an intuitive interface for managing network settings and monitoring performance |
| Mobile App Support | Allows you to manage your router and network settings from your smartphone or tablet |
| Automated Setup Wizards | Assists in configuring network settings automatically |
| Parental Controls and Security Settings | Simplifies the process of setting up parental controls and security features |
| Firmware Updates | Keeps your router’s software up to date with the latest features and security patches |
10. Customer Support
Some companies merely want to sell their product and provide generic technical assistance when an issue occurs. A good customer support makes a major difference between manufacturers. Before making a purchase, be sure to check out the brand’s blogs and contact us section to see how they assist customers.
Key Aspects of Customer Support
| Aspect | Function |
| Availability | Access to customer support when needed, including 24/7 support |
| Responsiveness | Quick response times to support requests and issues |
| Knowledge and Expertise | Access to knowledgeable and well-trained support staff |
| Online Resources | Availability of comprehensive online resources such as FAQs, user manuals, and guides |
| Warranty and Return Policy | Protection for your investment through warranties and return policies |
Conclusion
Since the routers available in the market have a very high variety, you need consider a number of variables to ensure that you obtain the right router for your purposes without going over budget. Don’t rely just on the seller’s claims because some pricey routers offer functions that you might never use. Additionally, many routers may have complex user interfaces that necessitate a technical specialist at all times, and you will always have to pay more for simple network changes. The price, coverage level, Wi-Fi standard, number of antennae, and port variety are, in my opinion, the most crucial factors to take into account when purchasing the finest home router.